Cotton fibre is of natural and plant origin. It is produced by a plant called the cotton plant which, after flowering, produces a capsule, known as a boll, containing seeds and fibres. These fibres are collected then used by the textile industry.
Key data
Type of fibre : natural plant fibre
Global annual production : approximately 25 million tonnes.
Main producer countries : China, India, United States and Pakistan (per order of production)
Place in global fibre production : 2nd place, equating to almost 25% of global production
Source : Preferred Fiber & Materials Market Report 2022 - Textile Exchange
Properties of the fibre and application examples
The properties of cotton fibre are numerous : Softness - Hypoallergenic - Resistance - Lightness - Absorption capacity - UV resistance.
Cotton is used in :
- clothing for babies, owing to its softness and hypoallergenic properties.
- jeans, owing to its resistance.
Can cotton be recycled? Yes, cotton-based products can be recycled mechanically (tearing, shredding, garnetting, fibre removal) or chemically (enzymatic dissolution).
ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACTS OF PRODUCTION
Significant use of pesticides
Every year, cotton production uses 20 000 tonnes of pesticides.
Very high water consumption
Between 5 000 and 17 000 litres of water to produce one kilo of cotton
Use of GMOs
Genetically modified cotton has an impact on the entire chain of living organisms surrounding it.
Pollution of soils, water and air
This pollution has a direct impact on the health of producers and neighbouring populations.
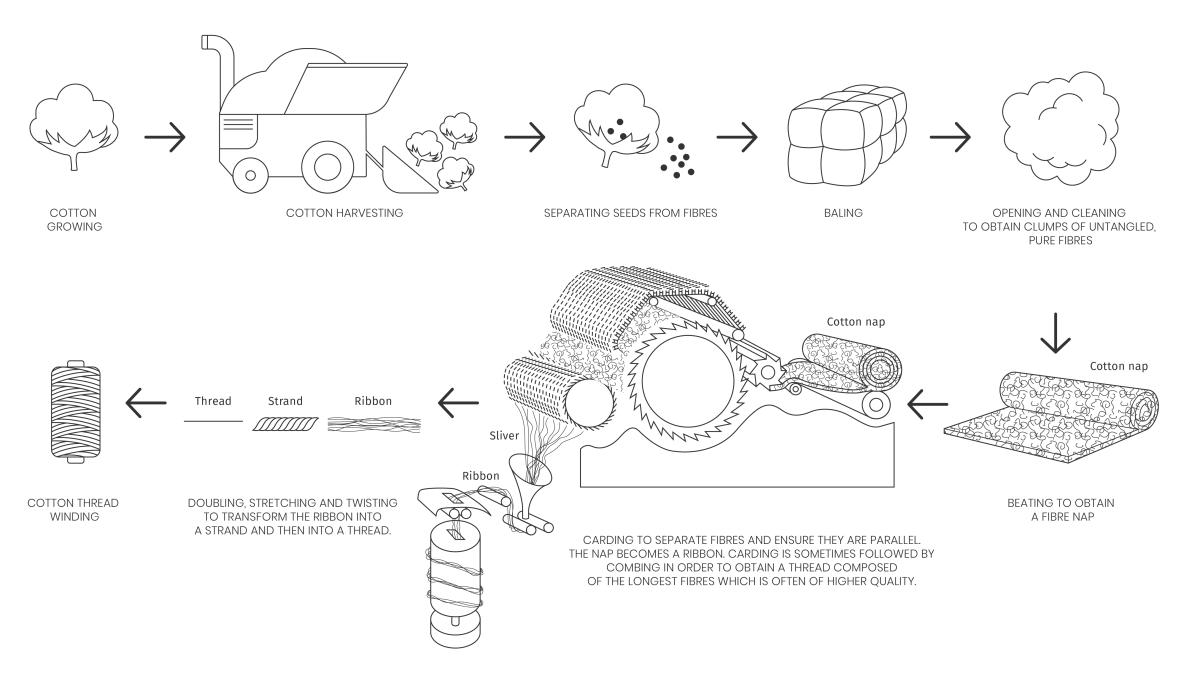
Transforming the cotton flower into thread involve numerous stages :
- The cotton plant is firstly grown and its flower harvested.
- Once the fibres are separated from the seeds, they are baled.
- Fibres are cleaned and untangled. A cotton nap is produced.
- This nap then follows the stages of spinning to obtain a thread: carding, combing, doubling, drafting, twisting.
- The cotton thread is wound around a spool and is ready to be used to produce fabric or knitwear for example.
Cotton production diagram
Disclamer : As in all eco-design approaches, before choosing a material, it is essential to analyze the environmental impact of the entire life cycle of a product and to compare different scenarios in order to identify which one is the most beneficial for the environment.
There is no ideal material, it is necessary to choose a material according to the environmental attributes that we want to give in our product.
Organic cotton
Organic cotton is produced and certified according to organic agricultural standards. Its production supports the wellbeing of soils, ecosystems and man by using natural processes as opposed to artificial inputs. Cultivating organic cotton does not permit the use of toxic chemical products and Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO).
Organic cotton production combines tradition, science and innovation in order to benefit from a shared environment and promote a good quality of life for all of the persons involved. Certain labels affixed to products namely certify that the products are composed, at least partly, of organic cotton. These labels namely include the European Ecolabel, Global Organic Textile Standard or BioRe. To find out more, consult the cheat sheet on Product Communication and Labels.
Source : Preferred Fiber & Materials Market Report 2022 - Textile Exchange

BCI cotton
Better Cotton Initiative is a non-profit making organisation which promotes sustainable and responsible production standards for cotton growing in 21 countries and among 2 million farmers. The initiative currently represents approximately 19 % of global cotton production.
Among the production principles and criteria, BCI namely encourages the minimisation of the harmful impacts of crop protection practices, the implementation of a good management system, the monitoring of soil wellbeing, the improvement of biodiversity thanks to responsible land management, the preservation of fibre quality and the encouragement of decent employment in order put in place an effective management system.
Source : Better Cotton Initiative

Recycled cotton
Recycled cotton is a material resulting from used clothing recycling (known as post-consumer) or from production off-cuts (known as pre-consumer).
Cotton can be recycled both mechanically and chemically. In addition to being used to recreate thread, there are numerous outlets for recycled cotton: paper-making, professional or household cleaning cloths, transformation into unwoven fabric or into fuel.
- Mechanical cotton recycling: to create a cotton thread via a mechanical recycling process, materials must firstly undergo fibre removal (stretched to recover the fibres). Given that mechanical fibre removal can and shorten fibres and make them fragile, they are often blended with virgin cotton or polyester to given them more resistance. Following this, fibres are ready to undergo a classic spinning process.
- Chemical cotton recycling: to create a cotton thread via a chemical recycling process, materials undergo enzymatic dissolution. This is an enzymatic treatment which decomposes polymers. Following treatment, the cellulose monomers are regenerated in order to re-form a filament. The filament can then undergo a classic spinning process.
Source : Map of Products Resulting from Used Textile Recycling
